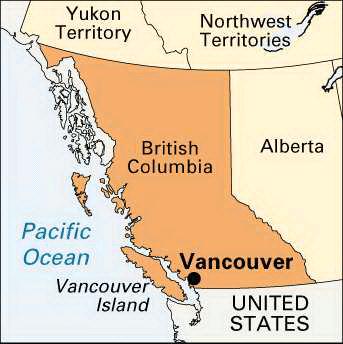
British Columbia-Vancouver
British Columbia is a province located on the west coast of Canada. The province's name was chosen by Queen Victoria when the Colony of British Columbia, i.e., "the Mainland," became a British colony in 1858. In 1871, it became the sixth province of Canada. Its Latin motto is Splendor sine occasu ("Splendour without Diminishment").
The capital of British Columbia is Victoria, the fifteenth-largest metropolitan region in Canada, named for the Queen who created the Colony of British Columbia. The largest city is Vancouver, the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada, the largest in Western Canada, and the second-largest in the Pacific Northwest. In October 2013, British Columbia had an estimated population of 4,606,371 and its land area is 944,735 km2. Annually, about 35,000 immigrants arrived in the province, which constitute an important part of the population.
British Columbia's economy is largely resource-based. It is the endpoint of transcontinental railways and the site of major Pacific ports that enable international trade. This province is agriculturally rich (particularly in the Fraser and Okanagan valleys) because of milder weather near the coast and in certain sheltered southern valleys. Its climate encourages outdoor recreation and tourism, though its economic mainstay has long been resource extraction, principally logging, farming, and mining. Vancouver, the province's largest city and metropolitan area, also serves as the headquarters of many of the western-based natural resource companies. It also benefits from a strong housing market and a per capita income well above the national average. While the coast of B.C. and certain valleys in the south-central part of the province have mild weather, the majority of B.C.'s land mass experiences a cold-winter-temperate climate similar to that of the rest of Canada. The Northern Interior region has a subarctic climate with very cold winters.
As previously mentioned, Vancouver is the largest city on the mainland of British Columbia. The 2011 census recorded 603,502 people in the city, making it the eighth largest Canadian municipality. The Greater Vancouver area of around 2.4 million inhabitants is the third most populous metropolitan area in the country and the most populous in Western Canada. 52 percent of its residents have a first language other than English. The City of Vancouver encompasses a land area of about 114 km2.
Vancouver is consistently named as one of the top five worldwide cities for livability and quality of life and the Economist Intelligence Unit acknowledged it as the first city to rank among the top-ten of the world's most livable cities for five consecutive years. Vancouver has been called a "city of neighbourhoods", each with a distinct character and ethnic mix.

Geography of British Columbia -Vancouver
British Columbia is bordered by the Pacific Ocean on the west side, by the American state of Alaska to the northwest and parts of the west, on the north by Yukon and the Northwest Territories, on the east by the province of Alberta, and on the south by the states of Washington, Idaho, and Montana. British Columbia's capital, Victoria, located at the southeastern tip of Vancouver Island. Only a narrow strip of the Island, from Comox to Victoria, is significantly populated. Vancouver which is the province's most populous city, located at the junction of the Fraser River and Georgia Strait, in the southwest corner of the province.
British Columbia has a mild, rainy oceanic climate. Due to the blocking presence of successive mountain ranges, the climate of the interior of the province is semi-arid with certain locations receiving less than 250 mm (10") in annual precipitation. The annual mean temperature in the most populated areas of the province is up to 12 °C, the mildest anywhere in Canada. Southern interior has short winters with only brief bouts of cold or rare heavy snow, while in the Central Interior, are colder because of increased altitude and latitude. Winters are generally severe in the Northern Interior.
Vancouver lies between Burrard Inlet to the north and the Fraser River to the south. The city has an area of 114 km2, including both flat and hilly ground. Until the city's naming in 1885, "Vancouver" referred to Vancouver Island, and it remains a common misconception that the city is located on the island. The island and the city are both named after Royal Navy Captain George Vancouver.
Vancouver has one of the largest urban parks in North America, Stanley Park, which covers 404.9 hectares. The North Shore Mountains dominate the cityscape, and on a clear day, scenic vistas include the snow-capped volcano Mount Baker in the state of Washington to the southeast, Vancouver Island across the Strait of Georgia to the west and southwest, and Bowen Island to the northwest.
Vancouver is one of Canada's warmest cities in the winter. Vancouver has a as Oceanic or Marine west coast climate. However, during summer months the inland temperatures are significantly higher, causing Vancouver to have the coolest summer average high of all major Canadian metropolitan areas.
Vancouver is also one of the wettest Canadian cities; however, precipitation varies throughout the metropolitan area. Annual precipitation as measured at Vancouver International Airport in Richmond averages 1,189 mm (46.8 in), compared with 1,588 mm (62.5 in) in the downtown area and 2,044 mm (80.5 in) in North Vancouver.
On average, snow falls on eleven days per year, with three days receiving 6 cm (2.4 in) or more. Average yearly snowfall is 38.1 cm (15.0 in) but typically does not remain on the ground for long. Average minimum temperature in the coldest and warmest months of the year in Vancouver is 0.5°C and 22 °C respectively.
History of British Columbia -Vancouver
British Columbia evolved from British Colonies that were established in what is now BC by 1871. First Nations, the original inhabitants of the land had a history of at least 10,000 years in the area. The first European has settled in Vancouver since 1862 and the City of Vancouver was incorporated on 6 April 1886.
Vancouver is located in the traditional territories of the Squamish, Musqueam, and Tseil-Waututh (Burrard) peoples of the Coast Salish group. They had villages in various parts of present day Vancouver, such as Stanley Park, False Creek, Kitsilano, Point Grey and near the mouth of the Fraser River. The first European to explore the coast of present-day Point Grey and parts of Burrard Inlet was José María Narváez of Spain, in 1791, although one author contends that Francis Drake may have visited the area in 1579. The Fraser Gold Rush of 1858 brought over 25,000 men, mainly from California, to nearby New Westminster on the Fraser River. A sawmill established in 1863, began the city's long relationship with logging. This mill, known as the Hastings Mill, became the nucleus around which Vancouver formed. The City of Vancouver was incorporated on 6 April 1886 and the city is named after George Vancouver, who explored the inner harbour of Burrard Inlet in 1792.
Iranian of Vancouver
Most of Iranian Canadian Citizens live in the municipalities of Vancouver such as: North Vancouver. Due to the resemblance of snow-capped Alborz Mountains in north of Tehran city with its luxurious villas, tree-lined streets, and large, well-kept parks with the Coast Mountains Vancouver’s high-rises and wide avenues many Iranians chose Vancouver to start a new life.
An estimated total of 29,265 reside in North Vancouver. Since 2002, the Iranian population in Vancouver has tripled. The Iranian community is well established. It has its own media, with the Farsi language Shahrvand e Vancouver (Citizens of Vancouver) being the main newspaper. Today, North Vancouver has many Persian restaurants and Farsi shop signs, with Iranian institutions like the recently-opened Deh Khoda School (named after a Persian philosopher) allowing children to study Farsi and Persian history.
Higher education in British Columbia-Vancouver
Higher education in British Columbia is delivered by 25 institutions that are consisting of eleven universities, eleven colleges, and three institutes. This is in addition to three private universities, five private colleges, and six theological colleges. There are also an extensive number of private career institutes and colleges.
According to reports in 2007, Approximately 433,000 people were enrolled in public post-secondary institutions in BC during the 2006-2007 academic years. More than 17,250 identified themselves as Aboriginal students and approximately 10,500 were international students.
Each of the province's post-secondary institutions sets its own admission requirements. Generally, successful graduation from high school, with the required academic prerequisites, is needed for admission to programs. Special consideration may be given to mature applicants, Aboriginal peoples, and people with disabilities.
The University of British Columbia is a public research university with campuses and facilities in the province of British Columbia, Canada. The McGill University College of British Columbia founded in 1908, the university became independent and adopted its current name in 1915. It is the oldest institution of higher learning in British Columbia and enrolls over 58,000 students at its Vancouver and Okanagan Valley campuses. UBC's area is about 4.02 km2 and located within the University Endowment Lands, which is about 10 km away from Downtown Vancouver.
UBC is ranked 30th in the world and eighth among universities outside the United States. UBC faculty, alumni, and researchers have won seven Nobel Prizes, 68 Rhodes Scholarships, 65 Olympic medals, 180 fellowships to the Royal Society of Canada.
The University of Victoria is a university in Canada. It is a research intensive university located in Saanich and Oak Bay within Greater Victoria, 5.71 km northeast of downtown Victoria, British Columbia. The university's annual enrollment is about 20,000 students. UVic's campus is known for its innovative architecture, beautiful gardens and mild climate. The university was closely affiliated with and established by McGill University, which is also credited with the beginnings of the University of British Columbia.
The university attracts many students in part because of its size, its picturesque location, and its cooperative education, earth and ocean sciences, engineering, and law programs. The university is the nation's lead institution in the VENUS and NEPTUNE deep-water seafloor observatory projects. In the 2014-2015, UVic is ranked 173th in the world and seventh place in Canada.
The University of the Fraser Valley is a Canadian public university with campuses in Abbotsford, Chilliwack, Mission and Hope, British Columbia. Founded in 1974 as Fraser Valley College, it was a response to the need for expanded vocational training in the communities of the Fraser Valley. In 1988, it became a university college, with degree-granting status.
In recognition of the growing needs for higher education within the region and in the province, the provincial government granted full university status on 21 April 2008. Student enrollment is now over 15,000 students annually.
Simon Fraser University is a public research university in Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada, with its main campus on Burnaby Mountain and satellite campuses in Downtown Vancouver and Surrey. The main campus area is about 1.7 km2 on Burnaby Mountain, located 20 km from downtown Vancouver, was established in 1965 and comprises more than 30,000 students and approximately 950 faculty members. The university was named after Simon Fraser, a North West Company fur trader and explorer. It is the only Canadian university competing in the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA).
SFU is ranked 24th from the 100 Under 50 universities 2014 in the world. SFU was ranked first among Canada's comprehensive universities in 1993, 1996-1998, 2000, 2008-2013 and in 2015.

Lifestyle in British Columbia -Vancouver
The cost of living in British Columbia varies depending on where you live. Vancouver is the most stressed in the spectrum of affordability of housing in Canada. In 2012, Vancouver was ranked the second most unaffordable in the world, rated as even more severely unaffordable in 2012 than in 2011. The city has adopted various strategies to reduce housing costs, including cooperative housing, legalized secondary suites, increased density and smart growth. As of April 2010, the average two-level home in Vancouver sold for a record high of $987,500, compared with the Canadian average of $365,141.
People in B.C. earn competitive wages and enjoy a high standard of living. The income will depend on Their education, experience and occupation. In 2011, the median family income in B.C. was $69,150. In 2013, British Columbians working full-time earned an average weekly wage of $1,020.54, compared to the national average of $1,013.92. The average hourly wage for full-time employees in the province was $25.73. B.C.’s minimum wage is $10.25 per hour.