Ontario Toronto
Ontario is Canada's most populous province by a large margin, accounting for nearly 40% of all Canadians. It is the second largest province in total area and fourth largest in total area. It is home to the nation's capital city, Ottawa, and the nation's most populous city, Toronto. In the 2011 census, Ontario had a population of 12,851,821 and with a land area of 908,607.67 km2, it had a population density of 14.1/km2 in 2011. In 2013, Statistics Canada estimated the province's population to be 13,537,994.
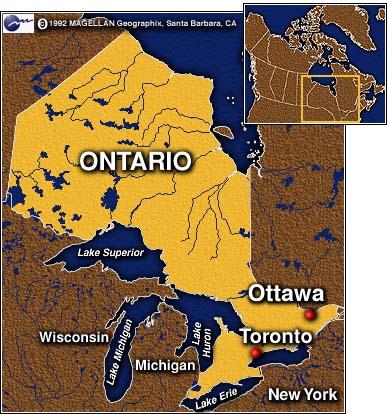
Ontario is bordered by the province of Manitoba to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay to the north, and Quebec to the east, and to the south by the U.S. states of Minnesota, Michigan, New York, Ohio and Pennsylvania.
Ontario is sometimes conceptually divided into two regions, Northern Ontario and Southern Ontario. The great majority of Ontario's population and its arable land are located in the south. In contrast, the larger, northern part of Ontario is sparsely populated.
Toronto is the most populous city in Canada and the provincial capital of Ontario. It is located in Southern Ontario on the northwestern shore of Lake Ontario, with the original city area lying between the Don and Humber rivers. According to the 2011 Census, the city had 2,615,060 residents while its census metropolitan area (CMA), which comprises the majority of the Greater Toronto Area, had a population of 5,583,064. It covers an area of 630 km2.
The majority of Ontarians are of English or other European descent including large Scottish, Irish and Italian communities. Immigration is a huge population growth force in Ontario, as it has been over the last two centuries. More recent sources of immigrants with large or growing communities in Ontario include Caribbeans, Latin Americans, Europeans, Asians, and Africans.
History of Ontario
The History of Ontario covers the period from the arrival of Paleo-Indians thousands of years ago to the present day. The lands that make up present-day Ontario, the most populous province of Canada as of the early 21st century, have been inhabited for millennia by groups of Aboriginal peoples, with French and British exploration and colonization commencing in the 17th century. Before the arrival of Europeans, the region was inhabited both by Algonquian and Iroquoian tribes. The French explorer (Étienne Brûlé) explored part of the area in 1610. The English explorer (Henry Hudson) sailed into Hudson Bay in 1611 and claimed the area for England.
On July 1, 1867 the Dominion of Canada were established, initially with four provinces: Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Quebec and Ontario. The Province of Canada was divided into Ontario and Quebec so that each linguistic group would have its own province.
When Europeans first arrived at the site of present-day Toronto, the vicinity was inhabited by the Iroquois people. The name Toronto is likely derived from the Iroquois word tkaronto, meaning "place where trees stand in the water". In 1867 Toronto was formally established as Ontario's provincial capital.
Economy of Ontario
Ontario is Canada's leading manufacturing province, comprising 52% of the total national manufacturing shipments in 2004. Ontario's largest trading partner is the American state of Michigan.
Ontario's rivers make it rich in hydroelectric energy. In 2009, Ontario Power Generation generated 70% of the electricity of the province, of which 51% is nuclear, 39% is hydroelectric and 10% is fossil fuel derived. By 2025, nuclear power is projected to supply 42%, while fossil fuel derived generation is projected to decrease slightly over the next 20 years. Much of the newer power generation coming online in the last few years is natural gas or combined cycle natural gas plants. An abundance of natural resources, excellent transportation links to the American heartland and the inland Great Lakes making ocean access possible via container ships, have all contributed to making manufacturing the principal industry, found mainly in the Golden Horseshoe region, which is the largest industrialized area in Canada, the southern end of the region being part of the North American Rust Belt. Important products include motor vehicles, iron, steel, food, electrical appliances, machinery, chemicals, and paper.
The North American Lexus RX is built in Cambridge. In 2013, Ontario was the largest manufacturer of automobiles in North America.
Ontario transcended Michigan in car production, assembling 2.696 million vehicles in 2004. Ontario has Chrysler plants in Windsor and Bramalea, two GM plants in Oshawa and one in Ingersoll, a Honda assembly plant in Alliston, Ford plants in Oakville and St. Thomas and Toyota assembly plants in Cambridge and Woodstock.
Ontario's steel industry was once centered on Hamilton harbor. Algoma Steel still maintains a plant in Sault Ste Marie.
Toronto, the capital of Ontario, is the center of Canada's financial services and banking industry. Neighboring cities are home to product distribution, IT centers, and various manufacturing industries. Canada's Federal Government is the largest single employer in the National Capital Region, which centers on the border cities of Ontario's Ottawa and Quebec's Gatineau.
Parliament Hill in Ottawa, home of the federal government. Canada's Federal Government is the largest single employer in the National Capital Region
The information technology sector is important, particularly in the Silicon Valley North section of Ottawa, as well as the Waterloo Region, where the world headquarters of Research in Motion (the developers of the BlackBerry smartphone) is located.
Hamilton is the largest steel manufacturing city in Canada, and Sarnia is the center for petrochemical production. Construction employed more than 6.5% of the province's work force in June 2011.
Mining and the forest products industry, notably pulp and paper, are vital to the economy of Northern Ontario. There has been controversy over the Ring of Fire mineral deposit, and whether the province can afford to spend CAD$2.25bn on a road from the Trans-Canada Highway near Kenora to the deposit, currently valued at CAD$60bn.
Tourism contributes heavily to the economy of Central Ontario, peaking during the summer months owing to the abundance of fresh water recreation and wilderness found there in reasonable proximity to the major urban centers. At other times of the year, hunting, skiing and snowmobiling are popular. This region has some of the most vibrant fall color displays anywhere on the continent, and tours directed at overseas visitors are organized to see them.
Toronto is an international center for business and finance. It is considered as the financial capital of Canada, Toronto has a high concentration of banks and brokerage firms on Bay Street, in the Financial District. The Toronto Stock Exchange is the world's seventh-largest stock exchange by market capitalization. The five largest financial institutions of Canada, collectively known as the Big Five, have national offices in Toronto.
The city is an important center for the media, publishing, telecommunication, information technology and film production industries; it is home to Bell Media, Rogers Communications, and Torstar. Other prominent Canadian corporations in the Greater Toronto Area include Magna International, Celestica, Manulife Financial, Sun Life Financial, the Hudson's Bay Company, and major hotel companies and operators, such as Four Seasons Hotels and Fairmont Hotels and Resorts.
Media in Toronto
Toronto is Canada's largest media market and has four conventional dailies, two alt-weeklies, and three free commuter papers in a greater metropolitan area of about 6 million inhabitants. The Toronto Star and the Toronto Sun are the prominent daily city newspapers, while national dailies, The Globe and Mail and the National Post are also headquartered in the city. The Toronto Star, The Globe and Mail, and National Post are broadsheet newspapers. Metro and 24 Hours are distributed as free commuter newspapers.
Toronto contains the headquarters of the major English-language Canadian television networks CBC, CTV, City, Global, The Sports Network (TSN) and Sportsnet. MuchMusic, MuchMore and MTV Canada are the main music television channels based in the city, though they no longer primarily show music videos as a result of channel drift.
Education in Ontario
In Canada, education falls under provincial jurisdiction. Elementary and secondary schools are administered by the Ontario Ministry of Education, while colleges and universities are administered by the Ontario Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities.
Higher education in Ontario includes postsecondary education and skills training regulated by the Ministry of Training, Colleges, and Universities and provided by universities, colleges of applied arts and technology, and private career colleges. The ministry administers laws covering 22 public universities, 24 public colleges (21 Colleges of Applied Arts and Technology and three Institutes of Technology and Advanced Learning), 17 privately funded religious universities and over 500 private career colleges. There are two central organizations that assist with the process of applying to Ontario universities and colleges: the Ontario Universities' Application Centre and Ontario College Application Service.
Toronto has a number of post-secondary academic institutions. The University of Toronto is Canada's largest university, has two satellite campuses, one of which is located in the city's eastern district of Scarborough while the other is located in the neighboring city of Mississauga. York University is Canada's third-largest university and located in the northwest part of the city. Toronto is also home to Ryerson University, OCAD University, and the University of Guelph-Humber.
There are four diploma and degree granting colleges in Toronto. These are Seneca College, Humber College, Centennial College and George Brown College. The city is also home to a satellite campus of the francophone Collège Boréal.
The Royal Conservatory of Music, which includes the Glenn Gould School, is a school of music located downtown. The Canadian Film Centre is a film, television and new media training institute founded by filmmaker Norman Jewison. Tyndale University College and Seminary is a Christian post-secondary institution and Canada's largest seminary.
The Toronto Public Library consists of 99 branches with more than 11 million items in its collection.
Official Languages of Ontario
The principal language of Ontario is English, which is spoken natively by about 70% of the province's population, according to the 2011 census. There is also a noteworthy French-speaking population concentrated in the northeastern and eastern parts of the province, where under the French Language Services Act. Immigrant languages such as Italian, Hindi, Gujarati, Tamil, Spanish, Chinese and Punjabi are also spoken in the province.
Geography of Ontario
The province consists of three main geographical regions; Canadian Shield in the northwestern and central portions, Hudson Bay Lowlands in the extreme north and northeast and Southern Ontario which is further sub-divided into four regions; Central Ontario, Eastern Ontario, Golden Horseshoe and Southwestern Ontario.
The climate of Ontario varies from season to season and from one location to another. It is affected by 3 air sources: cold, dry and arctic air from the north which is dominant factor during the winter months, and for a longer part of the year in far northern Ontario; Pacific polar air crossing in from the western Canadian Prairies/US Northern Plains and warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. In general, most of Ontario's climate is classified as humid continental. Ontario has three main climatic regions.
Toronto has a humid continental climate, with warm, humid summers and cold winters. The city experiences four distinct seasons, with considerable variance in day to day temperature, particularly during the colder weather season. It has a fairly low day-night temperature difference.
Toronto winters sometimes feature cold snaps where maximum temperatures remain below −10 °C. Snowstorms, sometimes mixed with ice and rain, can disrupt work and travel schedules, accumulating snow can fall any time from November until mid-April. However, mild stretches also occur in most winters melting accumulated snow. The summer months are characterized by long stretches of humid weather. Usually in the range from 23 to 31 °C, daytime temperatures occasionally surpass 35 °C accompanied by high humidity making it feel oppressive during these brief periods of hot weather. Spring and autumn are transitional seasons with generally mild or cool temperatures with alternating dry and wet periods.
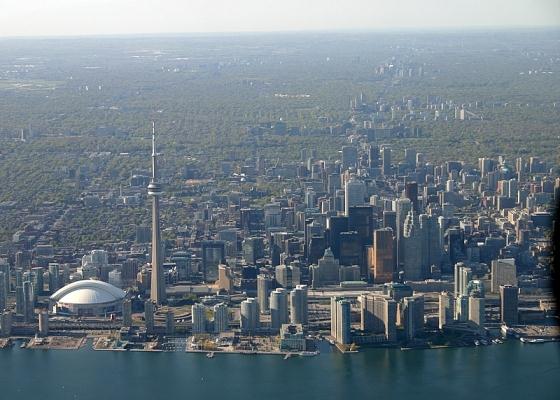

Downtown of Toronto
Downtown Toronto is the primary central business district in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Located entirely within the former municipality of Old Toronto, it is approximately bounded by Bloor Street to the north, Lake Ontario to the south, the Don River to the east, and Bathurst Street to the west. The area is made up of the city's largest concentration of skyscrapers and businesses. It also contains buildings of the municipal government of Toronto and provincial government of Ontario.
The Financial District centered on the intersection of Bay Street and King Street is the centre of Canada's financial industry. It contains the Toronto Stock Exchange, which is the largest in Canada and seventh in the world by market capitalization.